🚀 Best Practices for Evaluating the Qwen3-Next Model
Qwen3-Next is the next-generation foundational model in the Qwen series, achieving groundbreaking advancements in inference, instruction following, agent capabilities, and multilingual support. In this best practices guide, we will conduct a comprehensive evaluation using the EvalScope framework, taking the Qwen3-Next-80B-A3B-Instruct model as an example. This will cover both model service inference performance evaluation and model capability assessment.
Installing Dependencies
First, install the EvalScope model evaluation framework:
pip install 'evalscope[app,perf]' -U
pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git@main
Model Service Inference Performance Evaluation
To begin, we need to access the model's capabilities through an OpenAI API-compatible inference service for evaluation. Notably, EvalScope also supports model inference evaluation using transformers. For more details, refer to the documentation.
In addition to deploying the model to cloud services supporting the OpenAI interface, you can choose to launch the model locally using frameworks like vLLM or ollama. These inference frameworks can efficiently handle multiple concurrent requests, accelerating the evaluation process.
Below, we demonstrate how to launch the Qwen3-Next-80B-A3B-Instruct model service locally using vLLM and conduct performance evaluation.
Installing Dependencies
Using the vLLM framework (requires the nightly version of vLLM and the latest version of transformers), install the following dependencies:
pip install vllm --pre --extra-index-url https://wheels.vllm.ai/nightly
Launching the Model Service
The following command can be used to create an API endpoint at http://localhost:8801/v1 with a maximum context length of 8K tokens, utilizing tensor parallelism across 4 GPUs:
VLLM_USE_MODELSCOPE=true VLLM_ALLOW_LONG_MAX_MODEL_LEN=1 vllm serve Qwen/Qwen3-Next-80B-A3B-Instruct --served-model-name Qwen3-Next-80B-A3B-Instruct --port 8801 --tensor-parallel-size 4 --max-model-len 8000 --gpu-memory-utilization 0.9 --max-num-seqs 32
- Currently, the environment variable VLLM_ALLOW_LONG_MAX_MODEL_LEN=1 is required.
- The default context length is 256K. If the server fails to start, consider reducing the context length to a smaller value, such as 8000, and the maximum number of sequences to 32.
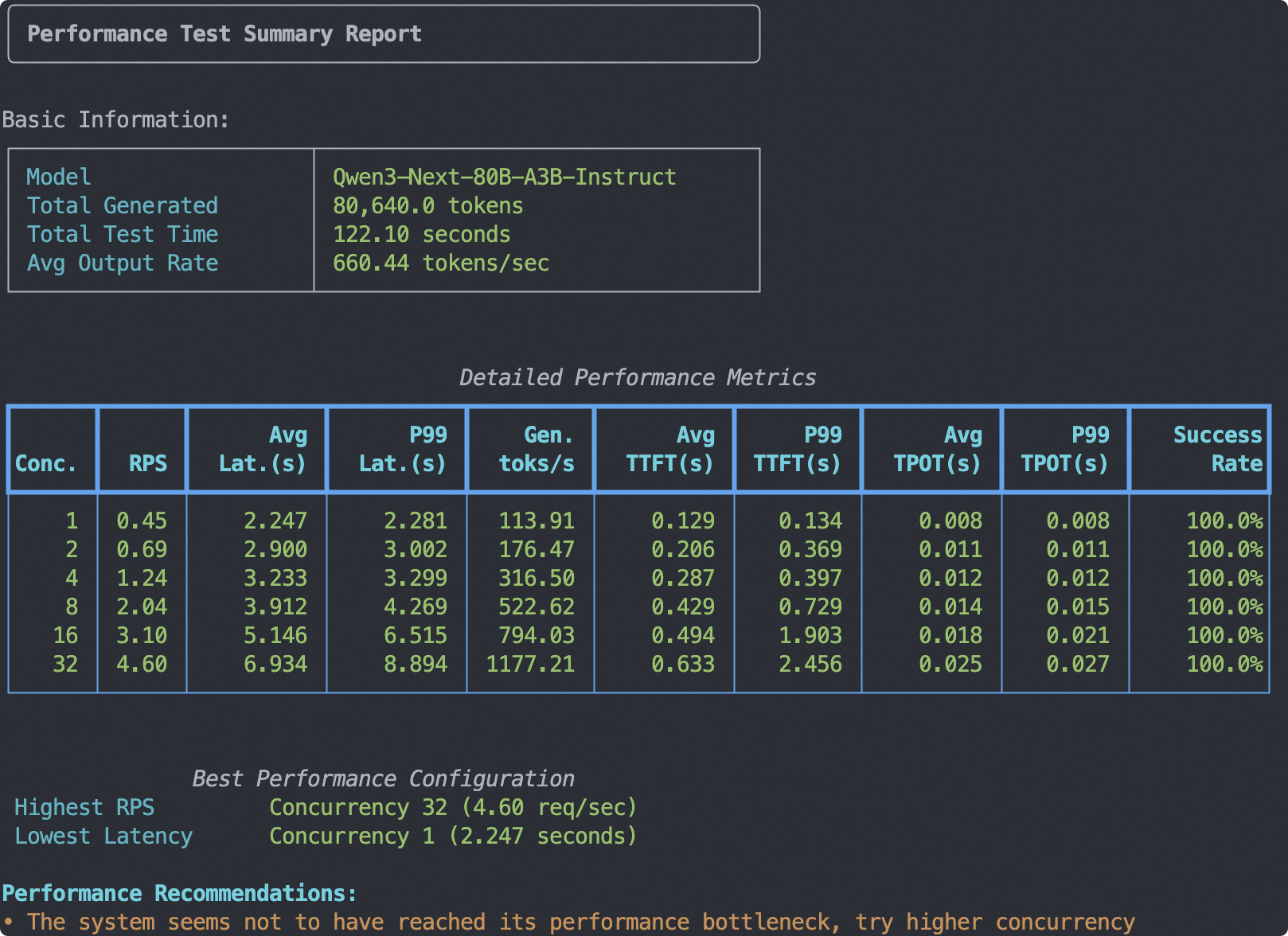
Conducting Stress Testing
- Test environment: 4 * A100 80G
- Test model: Qwen3-Next-80B-A3B-Instruct
- Test data: Randomly generated tokens of length 1024
- Test output length: 256 tokens
- Test concurrency: 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32
Run the following command:
evalscope perf \
--url "http://127.0.0.1:8801/v1/chat/completions" \
--parallel 1 2 4 8 16 32 \
--number 5 10 20 40 80 160 \
--model Qwen3-Next-80B-A3B-Instruct \
--api openai \
--dataset random \
--min-prompt-length 1024 \
--max-prompt-length 1024 \
--min-tokens 256 \
--max-tokens 256 \
--tokenizer-path Qwen/Qwen3-Next-80B-A3B-Instruct \
--extra-args '{"ignore_eos": true}'
For detailed parameter explanations, refer to Performance Evaluation.
Sample output:
Model Capability Evaluation
Next, we proceed with the model capability evaluation process.
Note: The subsequent evaluation process is based on the model service launched via vLLM. You can follow the steps in the previous model service performance evaluation to launch the model service or use a local model service. The model defaults to using the thinking mode.
Constructing an Evaluation Collection (Optional)
To comprehensively evaluate the model's capabilities, we can mix benchmarks supported by EvalScope to construct a comprehensive evaluation collection. Below is an example of an evaluation collection covering mainstream benchmarks, assessing the model's coding ability (LiveCodeBench), mathematical ability (AIME2024, AIME2025), knowledge ability (MMLU-Pro, CEVAL), and instruction following (IFEval).
Run the following code to automatically download and mix datasets based on the defined Schema, and save the constructed evaluation collection in a local jsonl file. You can also skip this step and directly use the processed data collection available in the ModelScope repository.
from evalscope.collections import CollectionSchema, DatasetInfo, WeightedSampler
from evalscope.utils.io_utils import dump_jsonl_data
schema = CollectionSchema(name='Qwen3', datasets=[
CollectionSchema(name='English', datasets=[
DatasetInfo(name='mmlu_pro', weight=1, task_type='exam', tags=['en'], args={'few_shot_num': 0}),
DatasetInfo(name='mmlu_redux', weight=1, task_type='exam', tags=['en'], args={'few_shot_num': 0}),
DatasetInfo(name='ifeval', weight=1, task_type='instruction', tags=['en'], args={'few_shot_num': 0}),
]),
CollectionSchema(name='Chinese', datasets=[
DatasetInfo(name='ceval', weight=1, task_type='exam', tags=['zh'], args={'few_shot_num': 0}),
DatasetInfo(name='iquiz', weight=1, task_type='exam', tags=['zh'], args={'few_shot_num': 0}),
]),
CollectionSchema(name='Code', datasets=[
DatasetInfo(name='live_code_bench', weight=1, task_type='code', tags=['en'], args={'few_shot_num': 0, 'subset_list': ['v5_v6'], 'extra_params': {'start_date': '2025-01-01', 'end_date': '2025-04-30'}}),
]),
CollectionSchema(name='Math&Science', datasets=[
DatasetInfo(name='math_500', weight=1, task_type='math', tags=['en'], args={'few_shot_num': 0}),
DatasetInfo(name='aime24', weight=1, task_type='math', tags=['en'], args={'few_shot_num': 0}),
DatasetInfo(name='aime25', weight=1, task_type='math', tags=['en'], args={'few_shot_num': 0}),
DatasetInfo(name='gpqa_diamond', weight=1, task_type='knowledge', tags=['en'], args={'few_shot_num': 0})
])
])
# get the mixed data
mixed_data = WeightedSampler(schema).sample(100000000) # set a large number to ensure all datasets are sampled
# dump the mixed data to a jsonl file
dump_jsonl_data(mixed_data, 'outputs/qwen3_test.jsonl')
Running the Evaluation Task
Run the following code to evaluate the performance of the Qwen3-Next model:
from evalscope import TaskConfig, run_task
task_cfg = TaskConfig(
model='Qwen3-Next-80B-A3B-Instruct',
api_url='http://127.0.0.1:8801/v1/chat/completions',
eval_type='openai_api',
datasets=[
'data_collection',
],
dataset_args={
'data_collection': {
'dataset_id': 'evalscope/Qwen3-Test-Collection',
'shuffle': True,
}
},
eval_batch_size=32,
generation_config={
'max_tokens': 6000, # Maximum number of tokens to generate, recommended to set a large value to avoid output truncation
'temperature': 0.7, # Sampling temperature (recommended value from Qwen report)
'top_p': 0.8, # Top-p sampling (recommended value from Qwen report)
'top_k': 20, # Top-k sampling (recommended value from Qwen report)
},
timeout=60000, # Timeout
stream=True, # Whether to use streaming output
limit=100, # Set to 100 data points for testing
)
run_task(task_cfg=task_cfg)
Sample output:
Note ⚠️: The results below are based on 100 data points and are only for testing the evaluation process. For formal evaluation, remove this limitation.
+-------------+---------------------+--------------+---------------+-------+
| task_type | metric | dataset_name | average_score | count |
+-------------+---------------------+--------------+---------------+-------+
| exam | acc | mmlu_pro | 0.7869 | 61 |
| exam | acc | mmlu_redux | 0.913 | 23 |
| exam | acc | ceval | 0.8333 | 6 |
| instruction | prompt_level_strict | ifeval | 0.6 | 5 |
| math | acc | math_500 | 1.0 | 4 |
| knowledge | acc | gpqa_diamond | 0.0 | 1 |
+-------------+---------------------+--------------+---------------+-------+
For more available evaluation datasets, refer to the Dataset List.
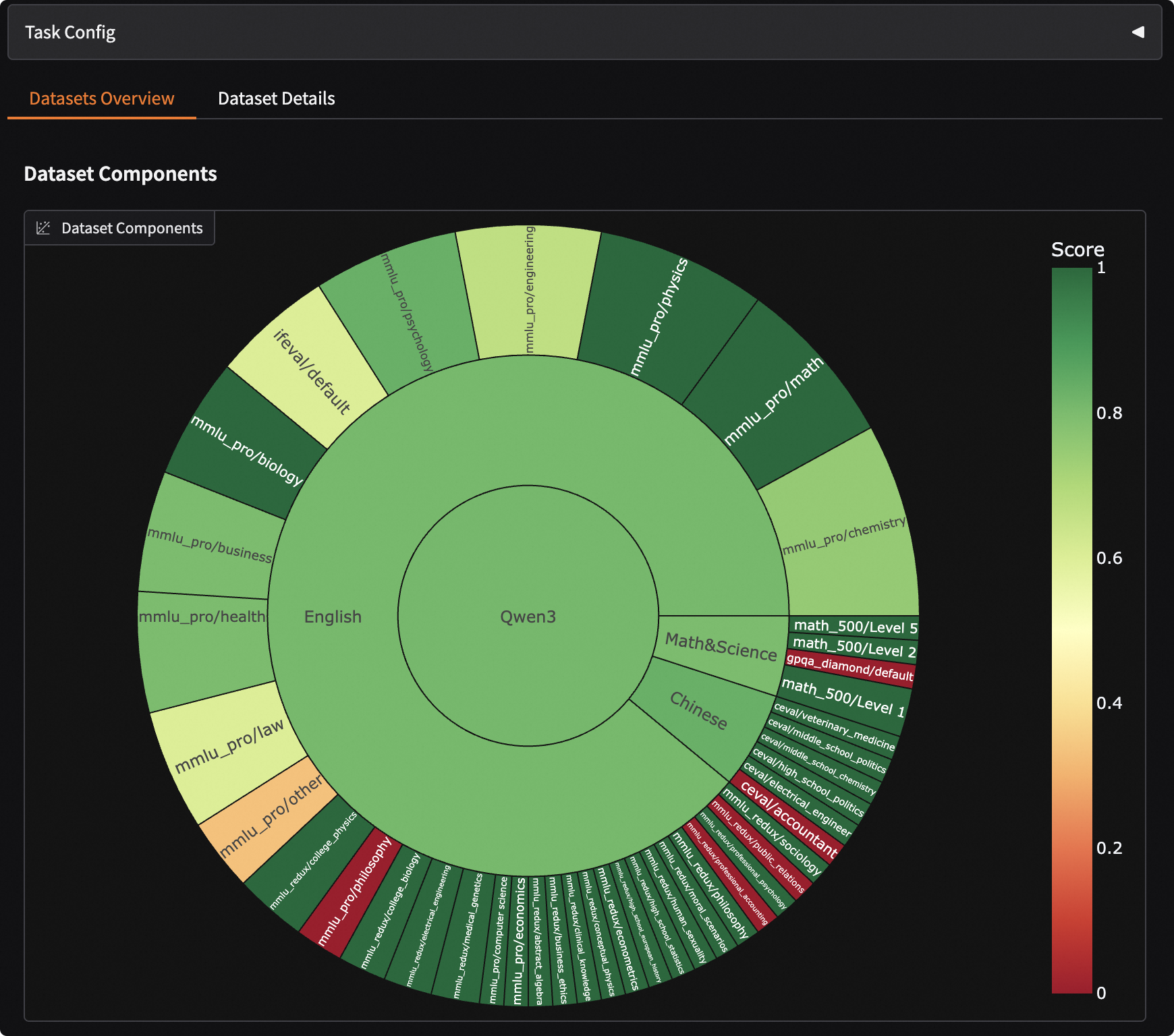
Visualizing Evaluation Results
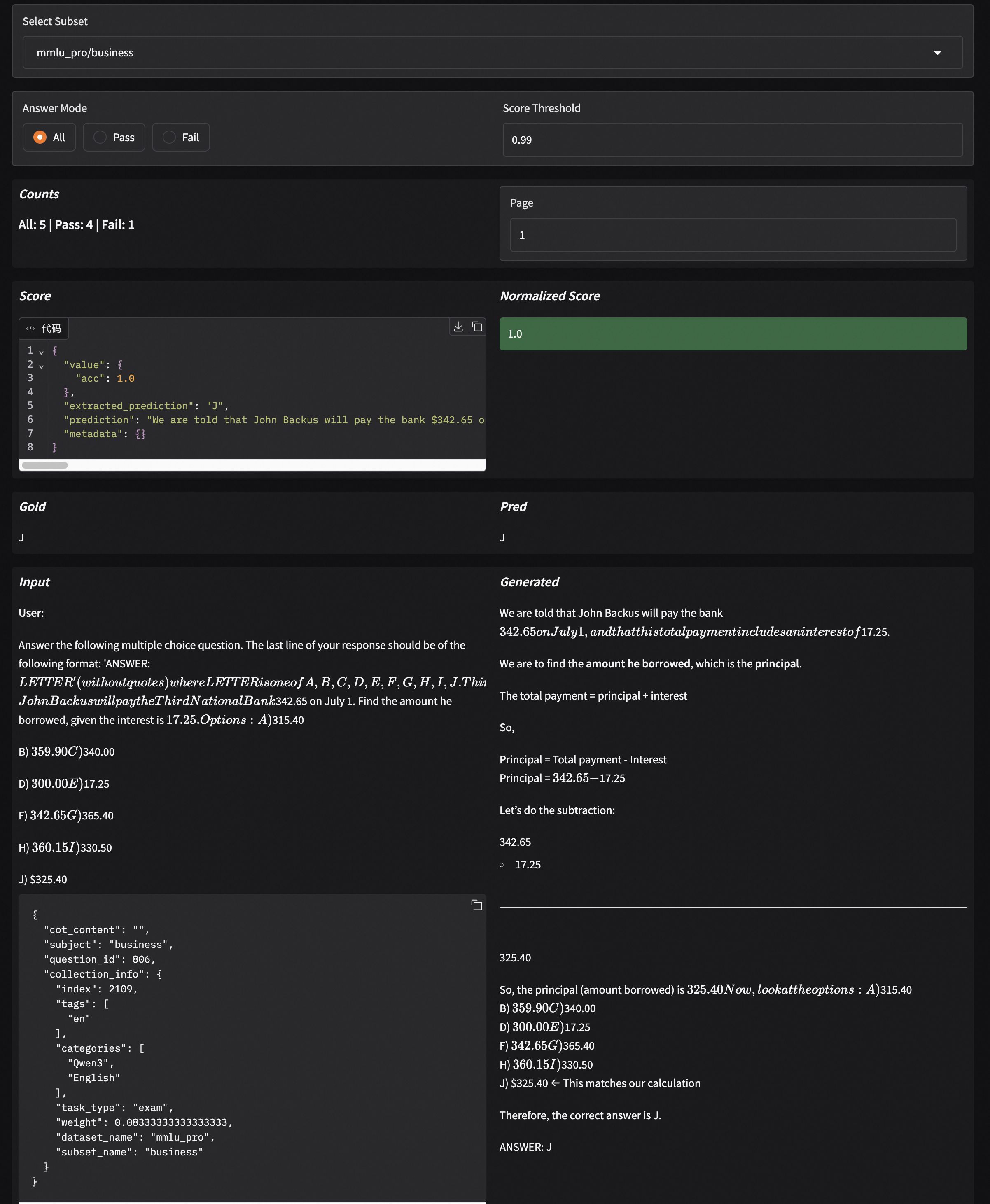
EvalScope supports result visualization, allowing you to view the model's specific outputs.
Run the following command to launch a Gradio-based visualization interface:
evalscope app
Select the evaluation report and click load to see the model's output for each question and the overall accuracy: